### Abstract Two Cross-Site Scripting vulnerabilities exists in the playlist functionality of WordPress. These issues can be exploited by convincing an Editor or Administrator into uploading a malicious MP3 file. Once uploaded the issues can be triggered by a Contributor or higher using the playlist shortcode. This issue was successfully tested on the WordPress version 4.5.3. #### Introduction WordPress is web software you can use to create a website, blog, or app. Two Cross-Site Scripting vulnerabilities exists in the playlist functionality of WordPress. These issues can be exploited by convincing an Editor or Administrator into uploading a malicious MP3 file. Once uploaded the issues can be triggered by a Contributor or higher using the playlist shortcode. #### Details It was discovered that meta information (ID3) stored in audio files are not properly sanitized in case they are uploaded by a user with the unfiltered_html (generally an Editor or Administrator). The first...
### Abstract Two Cross-Site Scripting vulnerabilities exists in the playlist functionality of WordPress. These issues can be exploited by convincing an Editor or Administrator into uploading a malicious MP3 file. Once uploaded the issues can be triggered by a Contributor or higher using the playlist shortcode. This issue was successfully tested on the WordPress version 4.5.3. #### Introduction WordPress is web software you can use to create a website, blog, or app. Two Cross-Site Scripting vulnerabilities exists in the playlist functionality of WordPress. These issues can be exploited by convincing an Editor or Administrator into uploading a malicious MP3 file. Once uploaded the issues can be triggered by a Contributor or higher using the playlist shortcode. #### Details It was discovered that meta information (ID3) stored in audio files are not properly sanitized in case they are uploaded by a user with the unfiltered_html (generally an Editor or Administrator). The first Cross-Site Scripting vulnerability exists in the function that processes the playlist shortcode, which is done in the `wp_playlist_shortcode()` method (/wp-includes/media.php). This method creates a `<noscript>` block for users with JavaScript disabled.  The method `wp_get_attachment_link()` does not perform any output encoding on the link text. Meta information from the audio file is used in the link text, rendering `wp_playlist_shortcode()` vulnerable to Cross-Site Scripting. The second Cross-Site Scripting issue is DOM-based and exists in the JavaScript file /wp-includes/js/mediaelement/wp-playlist.js (or /wp-includes/js/mediaelement/wp-playlist.min.js). The WPPlaylistView object is used to render a audio player client side. The method renderTracks() uses the meta information from the audio file in a call to jQuery's append() method. No output encoding is used on the meta information, resulting in a Cross-Site Scripting vulnerability. 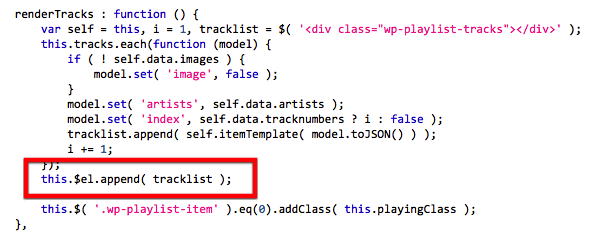 #### Proof of concept The following MP3 file can be used to reproduce this issue: [/advisory/SFY20160742/xss.mp3](https://securify.nl/advisory/SFY20160742/xss.mp3) 1) upload MP3 file to the Media Library (as Editor or Administrator). 2) Insert an Audio Playlist in a Post containing this MP3 (Create Audio Playlist).